The Hessian POW’s in Reading Revisited
They were Revolutionary War prisoners that no one wanted and the fledging American government could not afford to finance their care and well being
By HENRY J. RETZER
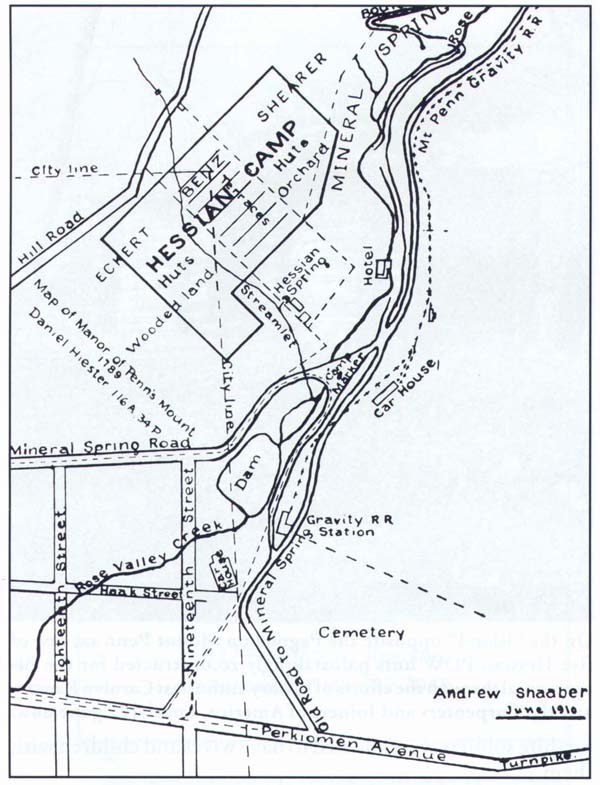
The presence of German prisoners of war in Reading, Pennsylvania, during the Revolutionary War has been covered by various authors since Andrew Schaaber in 1910 (“The Hessian Camp at Reading, Pa., 1781-83,” The Pennsylvania German, Aug., 1910). Larry Wildemuth elaborated on the encampment in 1970 (“Hessians and the Citizens of Reading.” Historical Review of Berks County), followed by George M. Meiser, IX, “Reading Hub of Continental Army,” (The Reading Eagle, May 17, 1978).
Since then several important items from the German point of view have been discovered. One is the journal of a Brunswick Grenadier, Johann Bense, kept during his stay in Reading. The other is a detailed letter of a Hessen-Hanau sergeant major, Samuel Vaupel, reporting on conditions in Reading to his former commanding officer in New York.
These two eye-witness accounts will form the basis of this article.
POW Johann Bense marched with the Duchy of Brunswick unit arriving in Reading on June 16, 1781. He began a journal almost immediately:
“On the bank of the Schuylkill, we had been camping on a meadow in the open air for 8 weeks and were plagued by the great heat during the day and by rain and cold during the night. On August 9, we marched from the Schuylkill via Reading onto a high, rocky mountain.
“We were supposed to build barracks there. But because we did not want to agree to that right away, but rather made ourselves straw huts, we were treated very severely. A sharp command from the corporal forced us to build the barracks and it was our good fortune because all our straw huts were consumed by fire on October 21, 1781.
“Therefore, those who had not yet completed their barracks, had to do more now to get them ready. Through that, the men got some freedom to go into the country and work and so they kept their supplies. They are read out twice a month [report for roll call twice a month].
“On April 26, 1782, we received money, linen trousers, shirts, and 1 pair of shoes from Lieutenant du Roi [of the Regiment Prinz Friederich]. Now, our situation was pretty good.
“It did not last long, however, that they locked us up and all who were in the country and worked there, had to come in [to the city].
“In the month of July, they read us an order from Congress. Any one of us wanting to be free, and that immediately, should give 80 silver talers [one British pound was worth 5 5/6 talers] as ransom and if he did not have that much money, a citizen should pay it for him with whom he should work in bondage for 3 years.
“But if we wished to enter service with them [in the American army], each would get 8 silver talers as gratuity and after the end of the war, he would be given 100 acres of land. This now was voluntary, to be sure, but because our men did not want to agree to that, we were treated very harshly.
“Since a few of us deserted, 356 men [of ours] were suddenly taken to the Reading jail and because there was not enough room, they had to lie in the court yard in the rain and the cold. They had to buy wood and water.
“Two hundred of our men were sent to the prison in Lancaster; the artisans were also taken there. Afterwards another 100 men were taken into prison, among them was myself. Because a few non-commissioned officers deserted, 42 sergeants and non-commissioned officers were also taken to jail. These had to lie in the cellar and below in the dungeon [at Lancaster]. Many of our men who could not stand it entered [American] service or sold themselves as indentured slaves for 3 years. The rest, who had been prisoners since September 11, were let out on December 16 but each had to give 1 taler.
“The non-commissioned officers were let out after 17 days but because some deserted right away again, those having been in jail before were quickly taken back to prison and had to remain there up to the exchange.
“Some of our men took up service on a pirate ship which was captured immediately at its departure from Philadelphia, and taken to New York. In the last year of our captivity, we thus were the most wretched and most miserable men. None of us could go out and none of the inhabitants were allowed to see us…
“On February 13, we had our first news of peace [from a Hessian Quartermaster]. We continued being in doubt until finally in March a French ship arrived in Philadelphia with the same message. It was made known to us at the barracks on the 26th that there was peace with France, Spain, Holland, and England and now we were daily hoping for our release. . . On April 16 in the afternoon, the non-commissioned officers came out of the city jail and [returned] to the barracks.
“On April 21, which was also the second day of Easter, at 12 Noon, 13 cannon shots were fired for the 13 free colonies. The whole city was illuminated in the evening and fires were made on April 24. In the morning the English Commissary Maclean came to give us each a blanket. Other staff officers came and we prisoners found out we would march to New York.”
(On May 1, Johann Bense acted as one of four sponsors of the son of fellow Grenadier Otto. The child received the name of Johann Conrad Ludwig Elias Otto. Bense departed Reading on May 3 and overnighted 19 miles away in Giettown [?]; the next night he reached Allentown. By May 10, 1783, he had arrived back in New York – a prisoner of war no longer. Ultimately, he was returned to the Duchy of Brunswick.)
The second eye-witness account of being held in the Reading prison camp comes from a lengthy letter written by a senior non-commissioned officer of a Hessen-Hanau unit: Sergeant-Major Samuel Vaupel. He was reporting to his commanding officer, one Lieutenant-Colonel Lentz, in New York:
“Your Excellency, I have a report to humbly send you, also a resolution from the Board of War of Congress and the address of Captain Thomas Bowen. From these, your Excellency will see in what a depressing situation we are in.
….. We were told everyone must choose to either buy himself free or join the American service. The king would not help us, and our prince did not want us… Nobody [from the ranks] responded to this reading and speech. It was immediately ordered that now nobody could leave camp and the proclamation read three times daily. But our people pretty much stuck together.
“On August 7, 1782, we were visited by Major-General [Benjamin] Lincoln and Brigadier-General [Moses] Hazen from Lancaster. The Corps had to form up and we were reviewed but they didn’t speak. They rode our regimental street and around the barracks, then went on to Reading.
“On the morning of the 10th instant, Brigadier-General Hazen returned with a German Captain [Anthony] Selin from his regiment. The troops had to turn out again and form a circle. The General spoke, which was translated by the above mentioned captain. We should choose to either make ourselves free by paying 80 Dollars or join the American army; the King of England did not care enough about us to exchange us or pay for our provisions; they cannot provide for us any longer when they have problems feeding their own men; and if we continue refusing to make our decision, serious measures will be taken.
“After the speech we NCOs said that we could not agree to these conditions, and asked if he would allow two NCOs from our Corps to go to New York to report these conditions to our commanding officer. If he says all hope is gone and doesn’t need us any longer, then every man can do as he wishes. The general’s answer was: He wanted to report it to Congress, but we have not heard anything as of now and don’t expect to.
“The above mentioned Captain Selin is Swiss-born and cannot be described badly enough; he was introduced to us as our commander. The new captain called together all the NCOs and gave orders that nobody will dare go 10 paces beyond the post without being termed a deserter and when the provost guard calls and they don’t stop, the guard should fire on them
“The water is located just outside the post, but nobody may go for it alone. The NCO of the guard has to call for water and one of his armed guards goes along to the well. This captain has ordered the guard to allow nobody out of camp, not even a woman or child, without permission. [Some of for-hire soldiers were allowed to have wives and children with them.]
“He also said he has forbidden the local residents into the camp. It is not permitted to openly bring us an apple. Since all this did not help, the above mentioned captain announced the NCOs were to blame for the lack of enlistments – that they discouraged the men from enlisting.
“This lasted until September 7, when he unexpectedly came to the barracks at daybreak and gave the order to march; our people were to go to the mountain with sack and pack. We all packed our things and when we were formed up on the barracks mountain, the captain went from right to left without saying anything. Finally, with the Brunswickers, he began pulling young people from the ranks.
“When he came to our regiment he only said the married men and NCOs should step forward. The remainder dressed ranks, were turned right and joined up with the Brunswickers to march to the jail in Reading.
“There were 142 men of our regiments and 158 Brunswickers, 300 in all. They filled up the jail and the remainder had to camp in the jail yard. The first day these people had to pay 2 pence for a pail of water and also had to pay for firewood to cook with. They were in this jail through the 10th instant.
“On the 11th instant 102 men from the regiment and 84 Brunswickers were taken to the jail in Lancaster.
“On the 24th instant, 21 men from the regiment and 25 Brunswickers were again taken to the jail in Lancaster. There is now nobody from the regiment in the Reading jail except the baker Muller from the Lt. Colonel’s Company.
“Private Wiskermann of the Leib Company was employed in Reading by a rich widow. On September 2, the captain had him brought in from the widow and asked him to enlist, buy himself free, or be sent to an underground prison or dungeon as the English call it. He decided he would rather be free and the above mentioned madam, named Mifflin, ransomed him.
“Fourteen men from the regiment who were employed at an iron smelter, have returned to the barracks. On September 23, 10 of these men were taken to the Reading jail. The other 4 men remained sick in the barracks; the other 10 men were taken, with others, on September 24 to Lancaster. They also had to each pay the jail keeper in Reading 1/4 Dollar for the one night lodging.
“Concerning us here in the barracks, we expect daily and hourly to go to the jail. Captain Selin indicated, when the others went to jail, that at the slightest incident or attempt at desertion, the others would also go into the jail. We have to hear daily from this captain how our tyrannical prince no longer needs us and that we will not get any more clothing or money from him. We collectively humbly beg your Excellency to have mercy on us and rescue us from this unhappy and depressing situation.
“Should this be impossible, we beg you to have the grace to send us uniforms, blankets, and money. Otherwise it will be impossible to withstand the coming winter as our blankets are torn and so little firewood is issued that we can’t make the fires small enough. . . nobody is allowed out to gather firewood.”
The efficient Sergeant-Major saw a need to include a paragraph on what was clearly a continuing problem with the hired mercenaries. He wrote: “The following musketeers here have married without consent: Johannes Schaeffer of Capt. Scheel’s Company, Phillip Emrich and George Meyer [or Mager?] of the Vacant Company; of the departed, Henrich Schilling of the Lt.-Col’s Company, Peter Hartman and Leon [hard] Muller of the Vacant Company were married before they departed.”
(Mrs. Leroy Sanders’ report, “Hessian and Brunswick Ancestry,” Historical Review of Berks County July/September issue, 1951, speaks directly to that point in having German POWs incarcerated in Reading’s “Hessian camp.”)
And what happened eventually to Sergeant-Major Samuel Vaupel? He’s listed on the Leib Company, Erbprinz Regiment of Hessen-Hanau, muster roll dated December 8, 1782, as having ransomed himself.

About the Author: Henry J. Retzer, of Hanover, PA, has been translating “Hessian” research for many years. He serves on the Editorial Board and the Board of Directors of the Johannes Schwalm Historical Association.